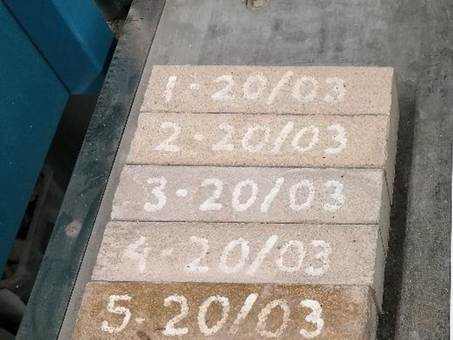Solution 1
Aerated Eco-Concrete Blocks
Partners
involved
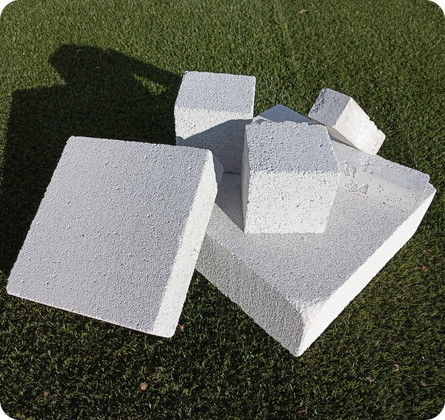




What are aerated eco-concrete blocks
Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks are versatile materials used in many construction applications. They are used for both load-bearing and non-load-bearing walls in residential and commercial buildings, as well as for interior partition walls. Additionally, AAC blocks can be used for floor and roof panels, exterior wall cladding, and even in infrastructural projects like bridges and tunnels. Their lightweight nature makes them particularly useful for building high-rise structures.
SNUG is focusing on a novel approach to producing autoclaved aerated eco-concrete (AAC) blocks using waste materials. The process, developed over an 18-month period, resulted in three distinct formulations, all of which successfully created aerated concrete blocks. These blocks are made of rectangular bricks with flat faces and undergo a multi-stage manufacturing process that includes foaming, pre-curing, and hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave before being dried.
To achieve our goals, we explored different component mixes, including ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS) and calcium carbide slag. Our novel approach successfully replaced traditional Portland cement, a key component in commercial AAC blocks, with more sustainable alternatives.
The primary goal was to develop a sustainable alternative to traditional AAC blocks by creating novel formulations using recycled waste products. This included:
- Developing new formulations that could serve as viable substitutes for commercial AAC blocks.
- Completely replacing Portland cement with ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS).
- Partially replacing the lime content with calcium carbide slag to further enhance sustainability.
- Ensuring that the new materials are maintained or improved upon the technical, safety, environmental, and economic properties of the commercial reference product.
The project’s outcomes have been highly successful and exceeded our expectations in several key areas:
- Formulation Development: We successfully developed three formulations. Formulations A and B have been optimized for large-scale industrial trials, while Formulation C, with its innovative and highly sustainable components, is proposed for future development.
- Material Substitution: We achieved a complete substitution of Portland cement with ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS), which significantly reduces the carbon footprint. Additionally, we successfully replaced 40% of the lime with calcium carbide slag. In one formulation (GEO A or B), we were able to use only 35% of the blast furnace slag compared to the cement amount in the reference product.
- Performance: The produced blocks demonstrated technical and safety properties that are comparable to the commercial reference product (400 kg/m³ density).
- Sustainability: Our newly developed materials showed significant improvements in environmental and economic indicators across all cases when compared to the commercial reference product.
Building on these promising results, the next phase of the project will focus on the following steps:
- Industrial Process Adjustment: The production process will be fine-tuned for an industrial-scale plant. This involves adjusting critical aspects of the complex manufacturing process, such as mix temperature, foam stability, and pre-curing time, to ensure consistency and quality at a larger scale.
- Fire Resistance Testing: Fire resistance, a critical safety property, has yet to be determined. We will conduct fire resistance tests on the blocks once they are produced in sufficient numbers at an industrial scale. This was not possible to do with the laboratory-scale samples.
- Addressing Challenges: Due to the lack of prior publications and experience with these novel formulations, the industrial scaling presents a considerable challenge. However, we are confident in our ability to address these issues and bring this innovative, sustainable solution to the market.