Solution 3
Aerogel-based solutions
Partners
involved




What is aerogel-based solutions
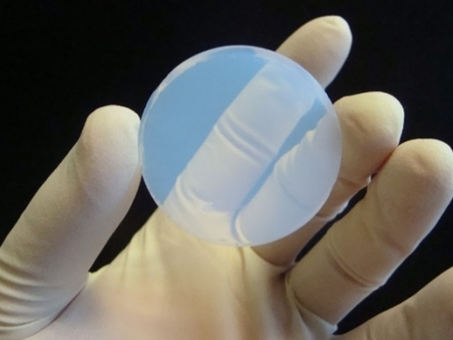
Aerogel-based solutions are advancing sustainable construction by utilizing the material’s unparalleled super-insulating properties, which come from its ultra-lightweight, nanoporous structure (up to 99.8% air) and resulting lowest thermal conductivity. This technology drastically boosts energy efficiency by minimizing the required thickness of insulation in a building’s envelope and windows, thereby cutting heating/cooling loads and associated carbon emissions. These solutions take the form of flexible aerogel blankets, insulating aerogel mortars, and aerogel-filled glazing, offering space savings, superior fire resistance, and hydrophobicity for both new builds and deep green renovations.
The SNUG project is developing two primary categories of insulation materials: recycled aerogel-based products and Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW)-based aerogel products. The goal is to obtain materials with high thermal performance comparable to commercial aerogels but with significantly lower embodied energy and carbon footprint by utilizing waste streams. The solutions include:
- Blown-in Insulation: Developed using waste from high-performance commercial aerogel insulation products (initially Pureflex, now Agitherm waste) and also using CDW-based aerogel granulates. These are intended for retrofitting wall cavities.
- Lime Plasters & Renders: Incorporating CDW-based aerogel to create insulation plasters for both modern and heritage building envelopes, offering high energy performance.
The overarching goals of the SNUG aerogel solutions are to:
- Improve Insulation Properties (Operational Energy): Achieve thermal performance (low lambda values) comparable to commercial aerogel insulation and outperform common market alternatives like glass wool and EPS beads.
- Increase Durability and Sustainability: Develop solutions with improved durability and contribute to the circularity of products by utilizing waste materials (Pureflex/Agitherm waste and CDW).
- Reduce Environmental Impact: Significantly reduces the exploitation of natural resources and energy consumed in the production process, leading to a substantial CO2 reduction.
- Lower Costs: Produce aerogel powder and granulates at a lower cost compared to commercial aerogels.
Significant progress has been made across the main product lines:
- CDW-Based Blown-in Insulation (Product 1): The optimized formulation of silica aerogel composites made from KEEY CDW aerogel granulates has been developed. Characterization shows the thermal conductivity of the final solution is comparable with commercial aerogel, meeting the technical performance key performance indicators (KPIs). The formulation also demonstrated the lowest water uptake.
- Lime Plasters (Product 2): A lime mortar incorporating commercial aerogel has been successfully developed and characterized. This reference product is applicable, has reasonable bonding, and a good lambda value.
- Recycling Waste Stream Optimization: After initial attempts with Pureflex (a PU-aerogel composite) waste showed poor performance (aerogel loss) under high-speed recycling, the project successfully switched to Agitherm (a melamine-based composite with aerogel). Agitherm retains its aerogel content, ensuring a consistent and high-performance blown-in insulation product.
- Novelty: Promising results were obtained in aerogel granulate composites from CDW, demonstrating similar performance to those currently on the market from natural silica resources.
The next steps for the SNUG aerogel solutions involve finalizing characterization, practical validation, and environmental assessment:
- Practical Validation (Endurance Testing): The lime plaster with commercial aerogel needs endurance testing in the SNUG demo house.
- Final Product Development (Plaster): The lime insulation plaster with KEEY CDW aerogel granules (PRODUCT 2) will be developed and characterized in the next period (WP3). The main challenge is obtaining improved binding properties to the wall while maintaining thermal performance.
- New Material Trials: Trials will be performed with the new Agitherm waste material for the blown-in insulation solution in the next period (WP3).
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): A first estimation of the embodied energy and carbon footprint reduction for the CDW-based solutions is expected during the next period.
- Further Characterization: Plasters with CDW aerogels are still pending further characterization.